Information Security
Information Security is concerned with protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of... View more
6 Unforgettable Lessons From the Equifax Data Breach [Updated 2022]
-
6 Unforgettable Lessons From the Equifax Data Breach [Updated 2022]
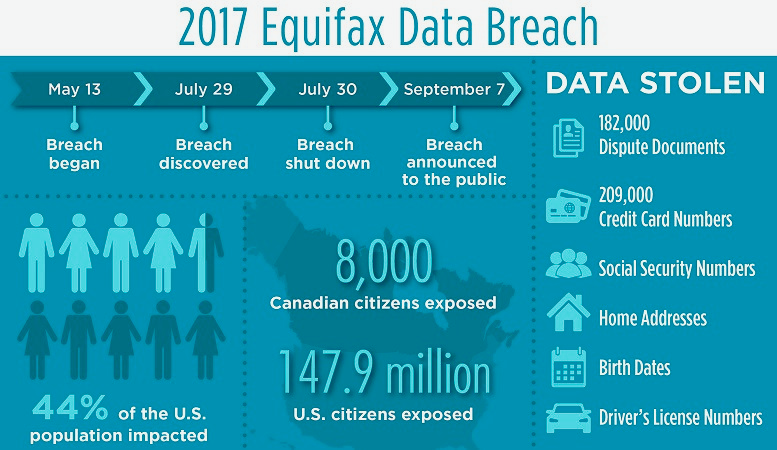
There’s a lot to know about the Equifax data breach of 2017. A Chinese state-sponsored hacker had stolen the personal information of at least 143 million Americans. The data breach went undetected for 10 months. The company paid the price for an unpatched system.
- Equifax was breached by Chinese state-sponsored hackers
On March 7, 2017, a group of Chinese state-sponsored hackers gained access to Equifax’s network and stole sensitive data. While the United States government’s Computer Emergency Readiness Team (CERT) had warned the company of the vulnerability, it did not implement a patching system. The attackers allegedly uploaded software allowing them to reconnaissance web systems and steal login credentials.
The hackers are accused of exploiting a vulnerability in Equifax’s dispute resolution website to access private customer data. They also broke into the company’s back-end databases. The hackers have been charged with a variety of crimes, including conspiracy to commit economic espionage, wire fraud, and computer fraud.
The breach is being investigated by the Justice Department, which is identifying a growing group of Chinese who are trying to steal American secrets. The hackers hacked the system of Equifax for weeks and routed their traffic through 34 servers in 20 countries. As a result, the breach exposed the private information of 147 million people.
The Chinese government has denied any involvement in the hack. However, the hack is a troubling sign of a deteriorating relationship between the two countries. In 2015, the Chinese government was implicated in a hack of the Office of Personnel Management, which compromised highly sensitive personal information of government workers. Other companies that recently disclosed breaches include the Marriott hotel chain and Anthem health insurance company.
- It was unpatched for at least 10 months
This data breach occurred when an Equifax employee failed to patch a critical vulnerability in its software. It’s not clear whether the problem was intentional or unintended, but the vulnerability wasn’t patched for at least 10 months. The data breach hit US consumers hard and damaged the US economy. The security breach was traced to an unpatched vulnerability in Apache Struts, which Equifax was using to verify the identity of potential customers who sought credit.
In the next few months, Equifax consulted Deloitte for a security audit. The audit found that Equifax had a history of security problems. Employees described vulnerabilities that went unpatched, poorly secured internal portals, and infrastructure that didn’t require two-factor authentication.
Equifax’s security problems were exacerbated by the fact that it had no formal method of verifying that patches were installed on its systems. Instead, the security team relied on an “honor system” to ensure that all patches were installed on Equifax systems. As a result, Equifax had a backlog of over 8,500 vulnerabilities. This meant that it didn’t know whether or not the security patches were installed on its networks, and thus wasn’t able to patch them until they were able to locate them.
A researcher discovered vulnerabilities in the Equifax system and discovered that the company had left thousands of servers exposed on the internet. Because of this, it had lost control of its infrastructure. Once the researcher identified the vulnerabilities, the company shut down its website in June.
- It cost Equifax a huge amount in settlements
The hackers got access to Equifax Inc.’s systems in mid-May, taking personal information that was stored on hundreds of database tables. The hack resulted in the theft of 147 million names, 145.5 million Social Security numbers, and 209,000 payment card numbers. Even now, the company is still trying to fix the damage.
The breach occurred because Equifax Inc. failed to implement basic security measures. For example, it failed to implement a policy to ensure that vulnerabilities in its servers were patched. Further, it failed to properly segment its database servers, which allowed hackers to operate undetected for long periods of time. Additionally, the company failed to install intrusion detection protections on its legacy databases. Furthermore, it allegedly stored passwords and network credentials in plain text.
While this data breach affected millions of people, Equifax decided to make some changes. First, they acquired an identity verification software company called Anakam. Anakam is based in San Diego, California, and invented SMS two-factor authentication. Equifax also agreed to reimburse those who lost money as a result of the breach.
Secondly, Equifax agreed to pay $300 million to a fund that would provide free credit monitoring services. This is in addition to the $125 million that would go towards compensation for consumers who had to pay out-of-pocket expenses as a result of the breach. The company also agreed to provide consumers with six free credit reports per year for seven years.
- It affected 143 million people
The Equifax data breach is the largest data breach in the history of consumer credit reporting. The hackers gained access to Equifax’s website from mid-May to mid-July, exploiting a flaw in its website software. The company only discovered the breach on July 29, and a month later it publicly announced the data breach. The company said that it found no evidence of unauthorized activity on its main databases, but that hackers were able to obtain names, birth dates, and addresses of 143 million people. It also said that 182,000 documents relating to personal disputes with individuals were stolen.
The Equifax data breach caused significant damage to many consumers. As a result, the company attempted to compensate consumers. It also offered free protection for a year, but the offer fell short of what consumers needed and deserved. Furthermore, the breach posed a significant national security threat. Chinese nation-state hackers had previously breached federal agencies, including Anthem, and they are working to build databases of Americans’ personal information to use in future attacks.
After the Equifax data breach was disclosed, many people began calling for the company to change its security practices. These improvements would make it more difficult for hackers to gain access to sensitive personal information. A cybersecurity expert says that companies should employ multiple layers of security to prevent hackers from stealing the crown jewels.
- You can freeze your credit report
A credit freeze is a legal measure you can take to protect yourself from identity theft and fraud. The freeze prevents people from looking at your credit, but it doesn’t prevent them from getting a copy of your report. It is also a convenient way to protect your privacy. Moreover, you can still access your credit reports, including free annual credit reports, a summary of your score, and other credit-related information. However, your current creditors, debt collectors, marketers, government agencies, and child-support agencies can still access your credit report. You can also grant permission for these agencies to check your credit.
A credit freeze does not affect your credit score, but it can delay major transactions, such as buying a new car or taking out a mortgage. However, freezing your credit can make it more difficult to obtain a loan or new credit card because you have to lift it each time you need to apply for a new line of credit. A freeze also means that you have to monitor your credit reports closely for fraudulent charges.
A credit freeze is an important precaution to take after the Equifax data breach. While the company declined to disclose the exact number of consumers who signed up, it is important to keep an eye on your personal information and sign up for fraud protection. However, be wary of scam callers who claim to be from Equifax and asking to verify information on your account.
- You should change your passwords
The Equifax data breach has exposed billions of user emails and passwords. If you have an account on one of the sites that have been affected, you should change your password on all of them. In addition, you should use strong passwords. Passwords should contain a mixture of upper and lower case letters, symbols, and numbers, and you should use different passwords for each account. It’s also a good idea to use a password manager.
The Equifax data breach occurred from May 2017 through July 2017. According to cybersecurity experts, it was the worst data breach in history. It compromised personal identifiers, including social security numbers. In addition, Equifax admitted using unencrypted servers. Changing your passwords after this breach is crucial to protect your personal information.
After the Equifax data breach, you should change your bank account and credit card information. Make sure to change your passwords, and change them frequently. Also, freeze your credit report to prevent hackers from opening new accounts with your personal information. You should also change any security questions that are associated with your accounts. You may also be asked to provide a new password for your credit card accounts. These are all ways for identity thieves to steal your personal information.
If you have gotten an email claiming that your information has been stolen, first confirm with the company that issued your personal information. Scammers are posing as the company that has been affected by the breach. It is best to confirm with the company itself through their website or phone.
Sorry, there were no replies found.