Information Security
Information Security is concerned with protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of... View more
10 Things You Must Know About the Dark Web [Updated]
-
10 Things You Must Know About the Dark Web [Updated]
It is a part of the web that isn’t visible to search engines, and requires an anonymous browser known as Tor to access. It’s a site where anyone can make a sale and interact with other people without fear of being discovered. It’s a fantastic location for communication and marketing however, it can also be an ideal location for illicit business. Learn more about this rising trend.
- Deep web versus dark web: are they different?
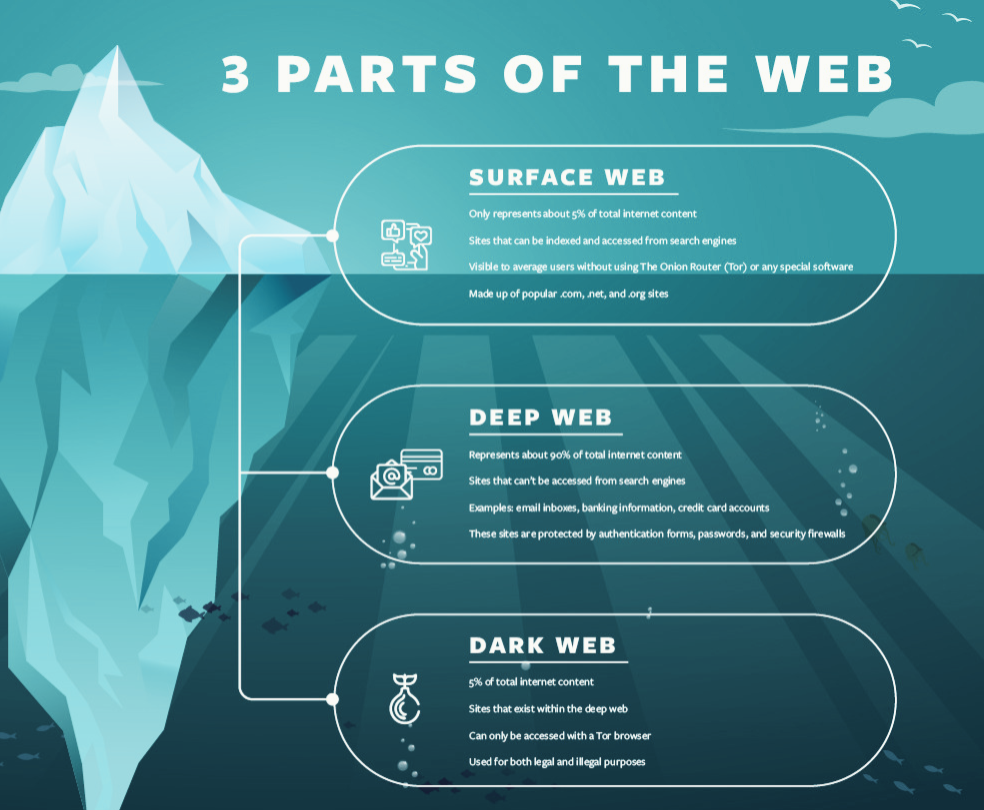
Though terms “deep web” and “dark web” are sometimes used interchangeably, they are not the same. Deep web refers to anything on the internet that is not indexed by a search engine like Google, and, therefore, not accessible by it. It typically includes anything behind a paywall or requires sign-in credentials. It also includes any content that its owners have blocked web crawlers from indexing.
Paid membership websites, password-protected applications, confidential company pages, and medical records, are just a few examples of what makes up the deep web. Estimates place the size of the deep web at more than 95% of the internet. Only a small portion of the internet is accessible through a standard web browser—generally known as the “surface web” or “clear web”.
The dark web is a hidden subset of the deep web that requires a specific browser called Tor to access. Most estimates put it at around 5% of the total internet.Read on to know more about this phenomenon!
2. What tools and services does the dark web have?
There exist 12 categories of tools or services that could present a risk in the form of a network breach or data compromise:
- Infection or attacks, including malware, distributed denial of service (DDoS) and botnets
- Access, including remote access Trojans (RATs), keyloggers and exploits
- Espionage, including services, customization and targeting
- Support services such as tutorials
- Credentials
- Phishing
- Refunds
- Customer data
- Operational data
- Financial data
- Intellectual property/trade secrets
- Other emerging threats
There exist three risk factors for each category:
- Devaluing the enterprise, which could include undermining brand trust, reputational damage or losing ground to a competitor
- Disrupting the enterprise, which could include DDoS attacks or other malware that affects business operations
- Defrauding the enterprise, which could include IP theft or espionage that impairs a company’s ability to compete or causes a direct financial loss
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) kits have been available on the dark web for several years, but those offerings have become far more dangerous with the rise of specialized criminal groups like REvil or GandCrab. These groups develop their own sophisticated malware, sometimes combined with pre-existing tools, and distribute them through “affiliates”.
The affiliates distribute the ransomware packages through the dark web. These attacks often include stealing victims’ data and threatening to release it on the dark web if the ransom isn’t paid.
This business model is successful and lucrative. IBM Security X-Force, for example, reported that 29% of its ransomware engagements in 2020 involved REvil. The criminal groups that developed the malware get a cut of the affiliates’ earnings, typically between 20% and 30%. IBM estimates that REvil’s profits in the past year were $81 million.
- Dark web browser
All this activity, this vision of a bustling marketplace, might make you think that navigating the dark web is easy. It isn’t. The place is as messy and chaotic as you would expect when everyone is anonymous, and a substantial minority are out to scam others.
The dark internet is accessible through use of an anonymous browser known as Tor. It routes your web page requests through a series of proxy servers operated by thousands of volunteers around the globe, making your IP address unidentifiable and untraceable. Tor works like magic, but the result is an experience that’s like the dark web itself: unpredictable, unreliable and maddeningly slow.
However, for those willing to endure the discomfort the dark web can provide an unforgettable glimpse into the murky underbelly of human condition – without the risk of running through the dark corners.
- Dark web search engine
Dark web search engines exist, but even the best are challenged to keep up with the constantly shifting landscape. The experience is reminiscent of searching the web in the late 1990s. Even one of the best search engines, called Grams, returns results that are repetitive and often irrelevant to the query. Link lists like The Hidden Wiki are another option, but even indices also return a frustrating number of timed-out connections and 404 errors.
- Dark web websites
Dark web websites look pretty much like any other site, but there are important differences. One is the naming structure. Instead of ending in .com or .co, dark web websites end in .onion. That’s “a special-use top level domain suffix designating an anonymous hidden service reachable via the Tor network,” according to Wikipedia. Browsers with the appropriate proxy can reach these sites, but others can’t.
Dark web websites also use a scrambled naming structure that creates URLs that are often impossible to remember. For example, a popular commerce site called Dream Market goes by the unintelligible address of “eajwlvm3z2lcca76.onion.”
Many dark websites are set up by scammers, who constantly move around to avoid the wrath of their victims. Even commerce sites that may have existed for a year or more can suddenly disappear if the owners decide to cash in and flee with the escrow money they’re holding on behalf of customers.
Law enforcement officials are getting better at finding and prosecuting owners of sites that sell illicit goods and services. In the summer of 2017, a team of cyber cops from three countries successfully shut down AlphaBay, the dark web’s largest source of contraband, sending shudders throughout the network. But many merchants simply migrated elsewhere.
The anonymous nature of the Tor network also makes it especially vulnerable to DDoS, said Patrick Tiquet, Director of Security & Architecture at Keeper Security, and the company’s resident expert on the topic. “Sites are constantly changing addresses to avoid DDoS, which makes for a very dynamic environment,” he said. As a result, “The quality of search varies widely, and a lot of material is outdated.”
- For sale on the dark web
The dark web has flourished thanks to bitcoin, the crypto-currency that enables two parties to conduct a trusted transaction without knowing each other’s identity. “Bitcoin has been a major factor in the growth of the dark web, and the dark web has been a big factor in the growth of bitcoin,” says Tiquet.
Nearly all dark web commerce sites conduct transactions in bitcoin or some variant, but that doesn’t mean it’s safe to do business there. The inherent anonymity of the place attracts scammers and thieves, but what do you expect when buying guns or drugs is your objective?
Dark web commerce sites have the same features as any e-retail operation, including ratings/reviews, shopping carts and forums, but there are important differences. One is quality control. When both buyers and sellers are anonymous, the credibility of any ratings system is dubious. Ratings are easily manipulated, and even sellers with long track records have been known to suddenly disappear with their customers’ crypto-coins, only to set up shop later under a different alias.
Most e-commerce providers offer some kind of escrow service that keeps customer funds on hold until the product has been delivered. However, in the event of a dispute don’t expect service with a smile. It’s pretty much up to the buyer and the seller to duke it out. Every communication is encrypted, so even the simplest transaction requires a PGP key.
Even completing a transaction is no guarantee that the goods will arrive. Many need to cross international borders, and customs officials are cracking down on suspicious packages. The dark web news site Deep.Dot.Web teems with stories of buyers who have been arrested or jailed for attempted purchases.
As in the real world, the price you pay for stolen data fluctuates as the market changes. According to Privacy Affair’s Dark Web Price Index 2021, these are the most current prices for some of the data and services commonly traded over the dark web:
- Cloned credit card with PIN: $25 to $35
- Credit card details with account balance up to $5,000: $240
- Stolen online banking logins with at least $2,000 in the account: $120
- PayPal transfers from stolen accounts: $50 to $340
- Hacked Coinbase verified account: $610
- Hacked social media account: $1 to $60
- Hacked Gmail account: $80
- Hacked eBay account with good reputation: $1,000
- Is the dark web legal?
We don’t want to leave you with the impression that everything on the dark web is nefarious or illegal. The Tor network began as an anonymous communications channel, and it still serves a valuable purpose in helping people communicate in environments that are hostile to free speech. A lot of people use it in countries where there’s eavesdropping or where internet access is criminalized.
If you want to learn all about privacy protection or cryptocurrency, the dark web has plenty to offer. There are a variety of private and encrypted email services, instructions for installing an anonymous operating system and advanced tips for the privacy-conscious.
There’s also material that you wouldn’t be surprised to find on the public web, such as links to full-text editions of hard-to-find books, collections of political news from mainstream websites and a guide to the steam tunnels under the Virginia Tech campus. You can conduct discussions about current events anonymously on Intel Exchange. There are several whistleblower sites, including a dark web version of Wikileaks. Pirate Bay, a BitTorrent site that law enforcement officials have repeatedly shut down, is alive and well there. Even Facebook has a dark web presence. More and more legitimate web companies are starting to have presences there. It shows that they’re aware, they’re cutting edge and in the know.
There’s also plenty of practical value for some organizations. Law enforcement agencies keep an ear to the ground on the dark web looking for stolen data from recent security breaches that might lead to a trail to the perpetrators. Many mainstream media organizations monitor whistleblower sites looking for news.
The dark web can also be a source of identity theft and drug trafficking. The FBI and other law enforcement agencies have focused on the sale of fentanyl on the dark web in the United States. Other activities that occur on the dark web include weapons and blueprint distribution. It’s difficult for authorities to track these types of websites and stop their activity. However, they’ve made some significant breakthroughs in recent years.
- Staying on top of the hacker underground
Some keen followers check in regularly if it’s important for them to be on top of what’s happening in the hacker underground. They use the dark web for situational awareness, threat analysis and keeping an eye on what’s going on. They want to know what information is available and have an external lens into the digital assets that are being monetized – this gives them insight on what hackers are targeting.
If you find your own information on the dark web, there’s precious little you can do about it, but at least you’ll know you’ve been compromised. Bottom line: If you can tolerate the lousy performance, unpredictable availability, and occasional shock factor of the dark web, it’s worth a visit. Just don’t buy anything there.
- It can be a marketing tool
Although the dark web is often associated with illegal activities, it’s also home to legitimate consumers who are looking for what you have to offer. One of the best examples of this is a website known as Dark Web News. The site has no traditional means of access and is intended for anonymous communication. However, marketers can harness the power of the dark web to find new markets and gather information about existing and potential customers.
Darknets include online forums and marketplaces. By identifying these spaces, marketers can identify the right niche and create a targeted marketing campaign. The key to using dark web marketing effectively is to know how to use it within your brand guidelines. It’s also important to know how to protect yourself and your brand.
For instance, the dark web has a lot of information about firearms. According to a study done by the Rand Corporation, almost 60 percent of the dark web firearms listings advertise products made in the US. However, European countries represent a much larger market and generate five times as much revenue as the US market. This means that there is a huge supply of firearms on the dark web.
- It can be a place for communication – either legit or criminal
The Dark Web is a place where internet users communicate anonymously. Users usually connect with one another using the Tor browser. This helps to keep the users’ identity and origin hidden. Because of this, users cannot tell who another user is, which makes Dark Web communication much more secure. This article looks at some of the common communication apps that users use on the Dark Web.
Most of the Dark Web’s communication tools have similar functionality to popular online chat services. Forums are easy to set up and use. Forum software is available for download from the Internet. However, forums hosted on the Dark Web are not safe from being hijacked from legitimate web servers. This can result in the servers being shut down by system administrators. Another popular form of communication on the Dark Web is IRC, which was popular in the 90s. Users could communicate with one another in real time and were anonymous.
There are also websites on the Dark Web dedicated to criminal activity. These include the Silk Road, an online marketplace for illegal goods. It was operated by Ross Ulbricht, who is currently in prison. He was charged with conspiracy, money laundering, drugs, and hacking. US federal investigators also broke a ring of fentanyl dealers in 2018 on the Dark Web. Meanwhile, two more dark web marketplaces were shut down by international police in 2019.
Besides being used by criminals, the Dark Web is also used by drug traffickers, terrorists, and counterfeit currency dealers. The Silk Road website alone made $1.2 billion worth of Bitcoin before it was shut down. Because criminals have more motivation to hide their identities, they are more likely to use the Dark Web for illegal activities.
Sorry, there were no replies found.